
It is defined as the ratio of the reflected voltage wave (Vr) to the incident voltage wave (Vi) at the interface: The reflection coefficient is typically denoted by the symbol "Γ" (gamma) and is a complex number. Let us understand Reflection coefficient formula and its calculator. It quantifies how much of an incident electromagnetic wave is reflected back from the interface, usually due to impedance mismatch, and how much is transmitted forward. when the wave travels from a material with a higher index of refraction to a material with a lower index of refraction.In RF (Radio Frequency) design, the reflection coefficient is a key parameter used to describe the behavior of electromagnetic waves at the interface between two transmission lines or components. To be clear, TIR and critical angles are only relevant when `n_2 < n_1`, i.e. Any incident angle greater than the critical angle won't result in any transmission at all. This means that the transmitted wave won't travel into the second material so much as along the interface between the two materials. It's worth mentioning that the critical angle is also where the angle of transmission is 90 degrees. The critical angle is given by the formula: In other words, it's the largest possible value of `theta_i` such that `theta_t = sin^(-1) (n_1/n_2 sin(theta_i) ) ` evaluates to an answer. Since `n_2 < n_1`, there an angle, called the Critical Angle 4, that is the largest incident angle that will still result in a transmitted wave. To see why, or at least when, this happens, let's look at Snell's Law rearranged to solve for `theta_t`. As the name suggests, TIR is when all of the incident is reflected, so no light transmits into the second material. If `n_2 < n_1`, there's an interesting phenomena termed Total Internal Reflection (TIR) 3. Both `theta_i` and `theta_t` are measured from the normal, but they're on opposite sides of the normal and interface. The Law of Refraction, commonly known as Snell's Law 2, is `n_1 sin(theta_i) = n_2 sin(theta_t)`. Both `theta_i` and `theta_r` are measured from the normal, but they're on opposite sides of the normal. As you can see, the angle of reflection is entirely independent of the indices of refraction of the two materials.
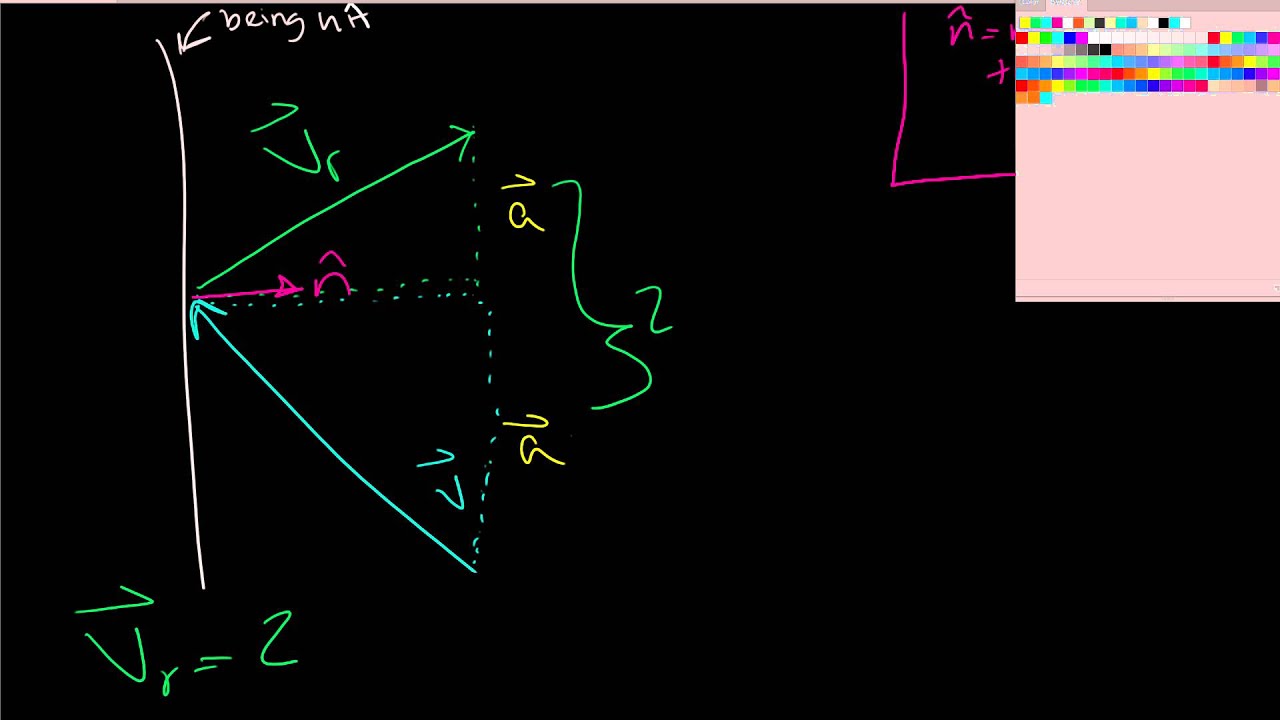
The Law of Reflection is fairly straightforward: `theta_i = theta_r` 1. The formula for Critical Angle between refraction and reflection is: The largest possible angle where of incidence that still result in refracted light is called the Critical Angle. The relationship can be seen in the following formula: Snell's law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or equivalent to the reciprocal of the ratio of the indices of refraction. The law is also satisfied in metamaterials, which allow light to be bent "backward" at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or transmission, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material. Snell's law (also known as Snell-Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and transmission, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In the picture, the horizontal line is the normal, and the vertical line is the interface between the two materials (between blue and white). The "normal" is a line perpendicular to the intersection of the two materials.

The angles are measured from the normal (see picture). Material 2 (red in the picture), where the light's going, is on the right. The light is coming in from material 1 (blue in the picture) on the left. The equations are solved for the incident, reflected, and transmitted angles and the materials' indices of refraction at the interface between two materials. The Angles of Reflection and Refraction Calculator provides calculations for reflection and refraction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
